Issue and approve certificates with Venafi Control Plane
Learn how to configure Venafi Control Plane, cert-manager, approver-policy-enterprise, and venafi-enhanced-issuer so that application teams can help themselves to SSL certificates which comply with enterprise PKI policy.
Create a Venafi Connection without Storing Secrets with TPP's JWT Mapping
This is a secretless method for authenticating with TLS Protect Datacenter (TPP). With this method, no access token nor password is needed. This method is limited to TLS Protect Datacenter (TPP) 22.4 and above. TLS Protect Cloud (VaaS) is not yet supported.
Now that you've installed all the prerequisite software in your cluster it's time to configure a Venafi Connection.
This job would typically be performed by the platform team.
The following example shows a Venafi Connection resource which uses a Kubernetes ServiceAccount Token to authenticate to Venafi TPP.
🔗 venafi-connection-1-jwt.yaml
# venafi-connection-1-jwt.yamlapiVersion: jetstack.io/v1alpha1kind: VenafiConnectionmetadata:name: application-team-1-connectionnamespace: jetstack-securespec:tpp:url: https://tpp1.example.comaccessToken:- serviceAccountToken:name: application-team-1audiences: ["tpp"]- tppOAuth:authInputType: JWTclientId: tls-protect-kubernetes # ⚠ This 'clientId' value has to match the value configured in TPPurl: https://tpp1.example.com
kubectl apply -f venafi-connection-1-jwt.yaml
⚠️ The VenafiConnection resource will not report any issues in its status as long as it is not used. Create an Issuer or CertificateRequestPolicy that references the VenafiConnection to start using the VenafiConnection, after which the VenafiConnection resource's status will be updated.
Create an example Issuer to debug our VenafiConnection with
Because the VenafiConnection is not used anywhere yet, its status will remain empty. To figure out if something is wrong with your connection and obtain the error details, we have to start using it. Therefore, we create an example issuer.
# venafi-example-issuer.yamlapiVersion: jetstack.io/v1alpha1kind: VenafiIssuermetadata:name: example-issuernamespace: jetstack-securespec:venafiConnectionName: application-team-1-connectionzone: \VED\Policy\Teams\application-team-1
kubectl apply -f venafi-example-issuer.yaml
Don't forget to remove this example issuer when you are done with all the steps below:
kubectl delete -f venafi-example-issuer.yaml
Create a Role and RoleBinding
If you use kubectl describe to view the status of the VenafiClusterIssuer resource you'll see an error:
$ kubectl -n jetstack-secure describe venaficonnection application-team-1-connection...Status:Ready Conditions:Last Transition Time: 2023-01-10T13:43:38ZMessage: connection is not ready yet (building connection failed): chain element 0 (ServiceAccountToken) error: serviceaccounts "application-team-1" is forbidden: User "system:serviceaccount:jetstack-secure:venafi-connection" cannot create resource "serviceaccounts/token" in API group "" in the namespace "jetstack-secure"Observed Generation: 1Operator Id: venafienhancedissuer.jetstack.ioReason: PendingStatus: False
This tells you that there's a problem with the first item in the accessToken field. The problem is that venafi-enhanced-issuer is trying to request a ServiceAccount token but it doesn't have permission. So first let's add a Role and RoleBinding to venafi-connection.yaml and reapply it:
# venafi-connection-2.yaml# create role that allows creating sa tokens for 'application-team-1'apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: Rolemetadata:name: create-tokens-for-application-team-1namespace: jetstack-securerules:- apiGroups: [ "" ]resources: [ "serviceaccounts/token" ]verbs: [ "create" ]resourceNames: [ "application-team-1" ]---# link the controller's service account to the 'create-tokens-for-vault-sa' roleapiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: RoleBindingmetadata:name: application-team-1-sa-rolebindingnamespace: jetstack-secureroleRef:apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.iokind: Rolename: create-tokens-for-application-team-1subjects:- kind: ServiceAccountname: venafi-connectionnamespace: jetstack-secure
kubectl apply -f venafi-connection-2.yaml
💡 Our controllers use exponential back-off between reconciliations in case a reconciliation error occurs. You can reset the exponential back-off timer by adding an annotation to the VenafiConnection resource, resulting in an immediate reconciliation.
kubectl -n jetstack-secure annotate venaficonnection application-team-1-connection last-trigger=$(date -u +"%FT%T.000Z") --overwrite
Create a ServiceAccount
If you use kubectl describe to view the status of the VenafiClusterIssuer resource again you'll see a different error:
$ kubectl -n jetstack-secure describe venaficonnection application-team-1-connection...Status:Ready Conditions:Last Transition Time: 2023-01-10T13:45:41ZMessage: connection is not ready yet (building connection failed): chain element 0 (ServiceAccountToken) error: serviceaccounts "application-team-1" not foundObserved Generation: 1Operator Id: venafienhancedissuer.jetstack.ioReason: PendingStatus: False
Add a ServiceAccount to venafi-connection.yaml and reapply:
# venafi-connection-3.yaml# create a ServiceAccount which will be used to authenticate to Venafi TPPapiVersion: v1kind: ServiceAccountmetadata:name: application-team-1namespace: jetstack-secure
kubectl apply -f venafi-connection-3.yaml
💡 Our controllers use exponential back-off between reconciliations in case a reconciliation error occurs. You can reset the exponential back-off timer by adding an annotation to the VenafiConnection resource, resulting in an immediate reconciliation.
kubectl -n jetstack-secure annotate venaficonnection application-team-1-connection last-trigger=$(date -u +"%FT%T.000Z") --overwrite
Configure Venafi TPP
Assuming that you've configured the TPP Mapping, the issuer should be able to connect to authenticate to Venafi TPP.
And assuming that the PolicyDN is correct and the user account has permission to read and write to that policy folder, the example VenafiIssuer resource should be Ready.
$ kubectl -n jetstack-secure get venafiissuer example-issuerNAME READY REASON MESSAGE LASTTRANSITION OBSERVEDGENERATION GENERATION AGEapplication-team-1 True Checked checked 64s 1 1 67s
Known errors
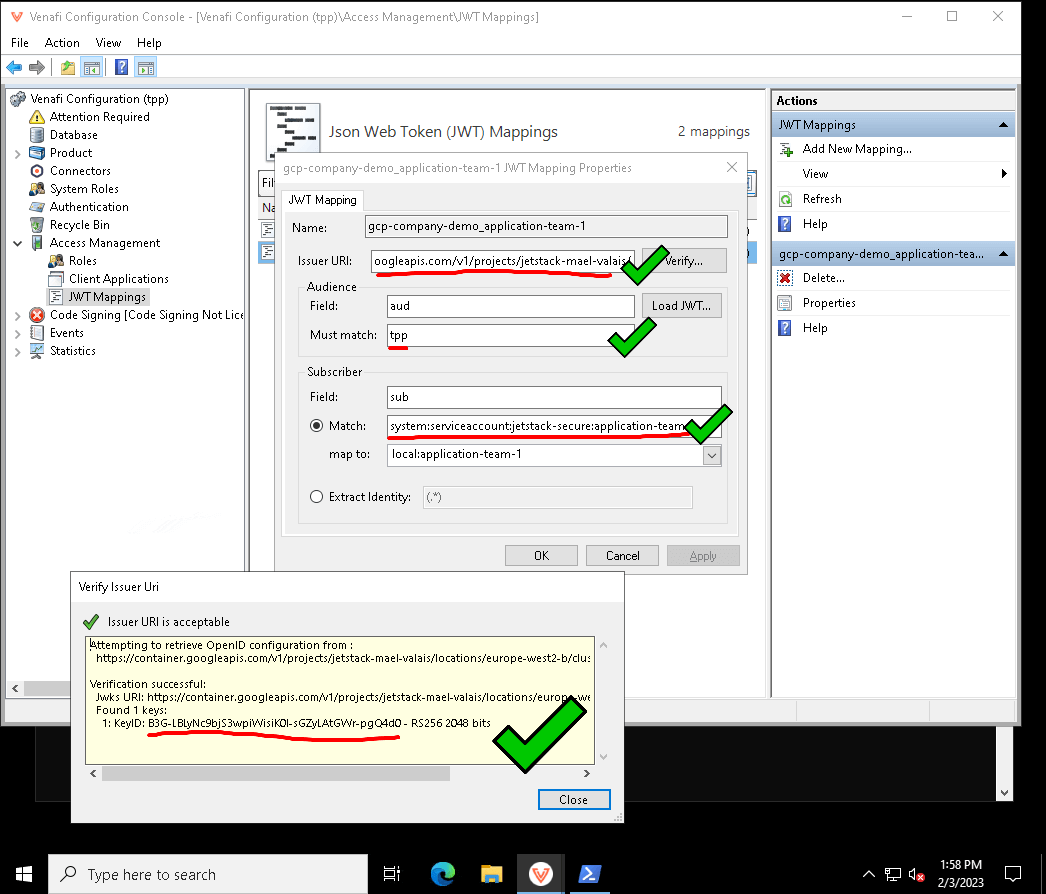
HTTP 400: unauthorized_client: Key ID XXXX not configured
The Key ID corresponds to the kid field in the JWT, and corresponds to the public key identifier.
When this message shows, it means that the JWT's kid did not match any of the public key IDs that TPP knows about. To check that the JWT Mapping in TPP knows about this kid, you can open the Venafi Configuration Console and click "Verify...". For example, in the following two screenshots, you can see that the Key ID found by TPP (top screenshot) matches the kid in the JWT (bottom screenshot).
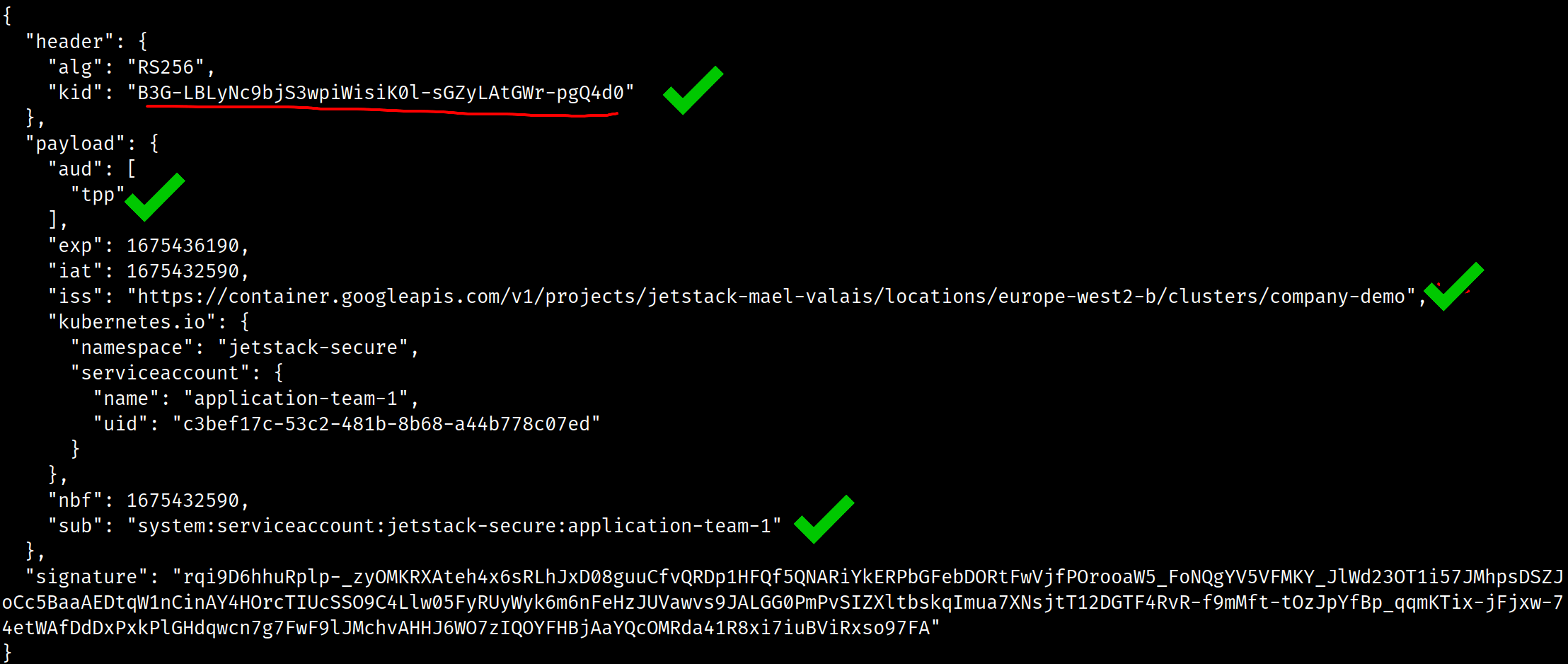
To see the kid in the JWT, you can use the step CLI:
kubectl create token --audience=tpp -n jetstack-secure application-team-1 \| step crypto jwt inspect --insecure
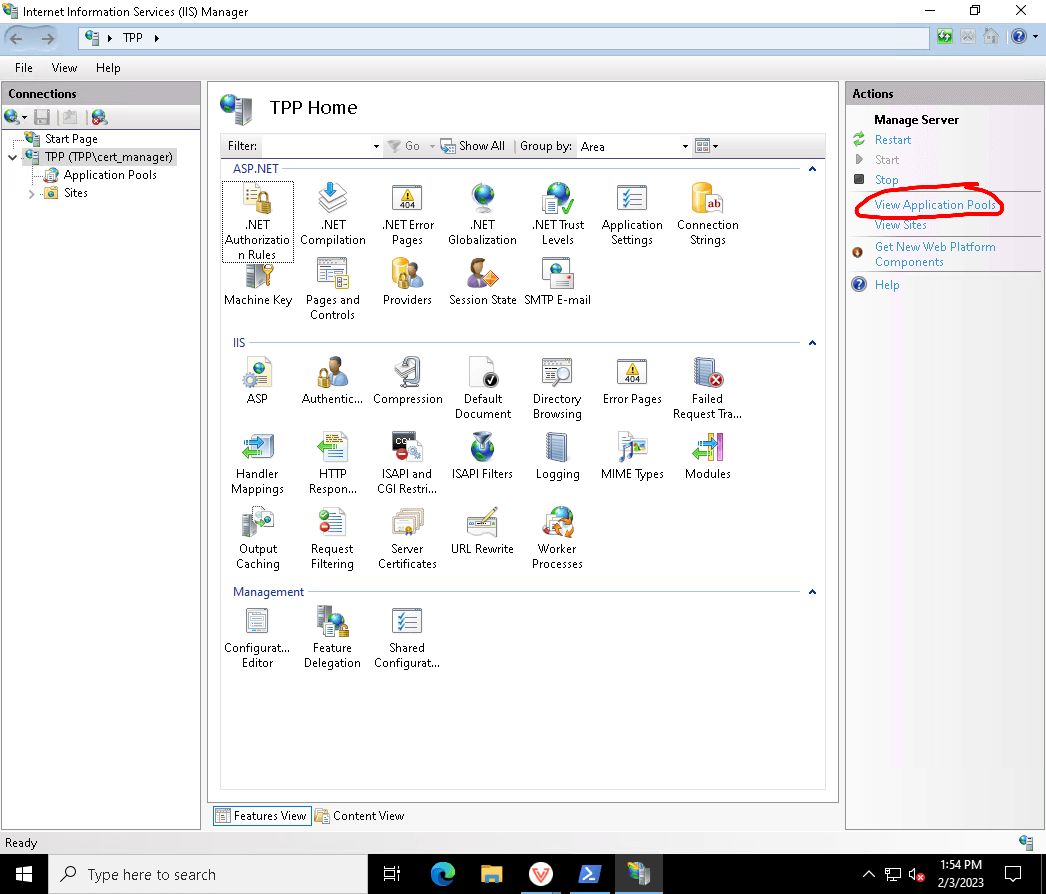
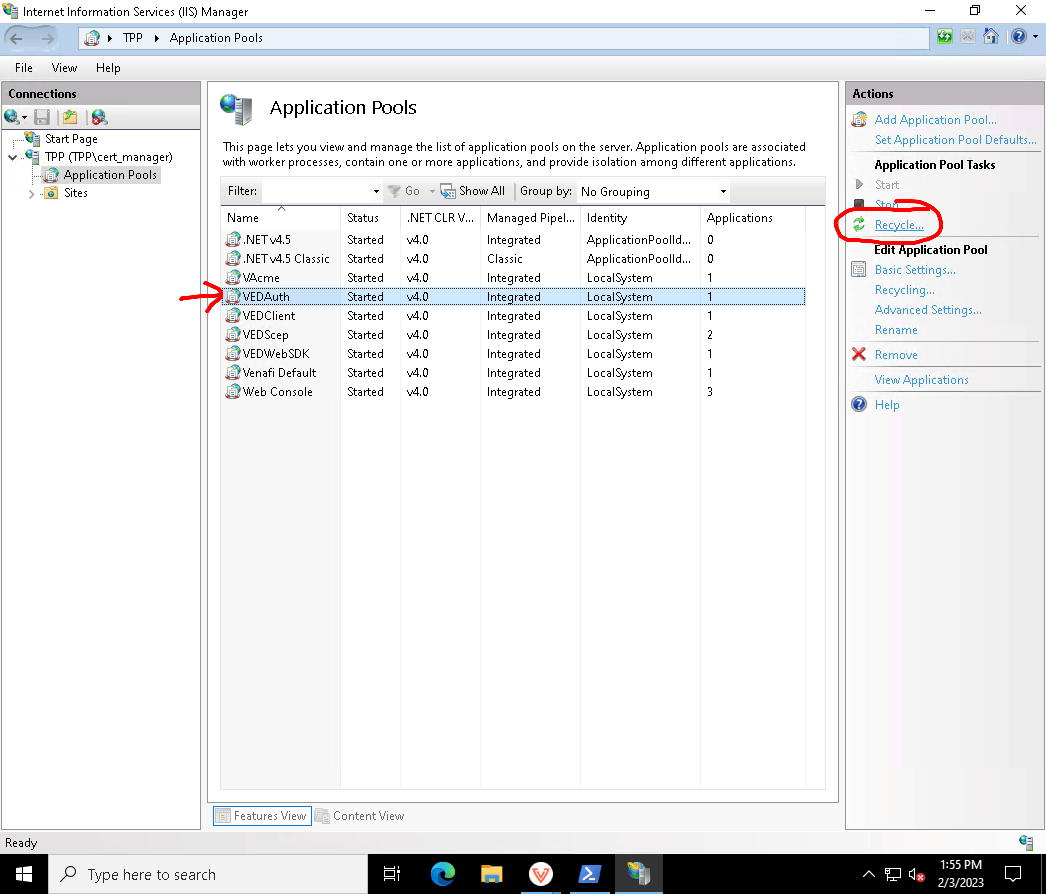
If the key IDs don't match, it might mean that TPP hasn't fetched the public key from the issuer URL yet. You can wait for 5 minutes, or recycle the VEDAuth application pool in IIS:
HTTP 400: unauthorized_client: No matching mappings for provided JWT
This means that there is an audience or subject mismatch between the JWT token and the JWT Mapping.
HTTP 400: invalid_scope:
This means that there is something off with the API Integration in TPP. Check that the API Integration tls-protect-kubernetes has the certificate:manage,revoke scope.
